An erect chest x-ray is probably the most sensitive plain radiograph for the detection of free intraperitoneal gas. if a large volume pneumoperitoneum is present, it may be superimposed over a normally aerated lung with normal lung markings. subdiaphragmatic free ray intra air abdominal free x gas. leaping dolphin sign. cupola sign (on supine film). An abdominal series (supine and upright abdominal x-rays and chest x-rays) may be diagnostic, showing free air under the diaphragm in 50 to 75% of cases. as time passes, this sign becomes more common. a lateral chest x-ray is more sensitive for free air than a posteroanterior x-ray.
Worst City For Allergies
There is evidence of intra-abdominal free air on both the ap and lateral images. diagnosis: the abdominal x-ray supports the clinical diagnosis of a paralytic ileus secondary to an intra-abdominal abscess. Free air seen on x-ray of abdomen itself is not threatening. but it needs a serious consideration as most of the time the underlying disease condition which produces it is life threatening. patient may also have other accompanying symptoms of the disease such as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, low blood pressure etc. patient looks sick.
Free Intraabdominal Air Without Peritoneal Perforation After
X-ray radiation is used in a variety of places. while it can be helpful, there are also risks. here are five things to know about x-ray radiation. advertisement by: marianne spoon wilhelm roentgen stumbled upon the potential of x-rays while. An abdominal x-ray series reveals distended loops of small bowel and large bowel without air fluid levels and no free air under the diaphragm. an abdominal ultrasound demonstrates a distended gallbladder with pericholecystic fluid and no stones. We report on two patients who demonstrated intra-abdominal free air on an erect chest x-ray after tem procedure without other findings of a pneumoperitoneum. we hypothesize that due to the combination of elevated pressures in the retroperitoneal cavity and decreased integrity of the retroperitoneal barrier, insufflated co2 gas can diffuse into the intraperitoneal cavity.
Fat Stranding Summary Radiology Reference Article
Learn how an x-ray works to diagnose thousands of medical conditions every day. discover the many uses for x-rays and how they benefit the medical field now. An erect chest x-ray showed both intra-abdominal free air and subcutaneous emphysema. intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics were started (ceftriaxone 1dd 2 gr, metronidazol 3dd 500 mg). after an initial rise in c-reactive protein with a maximum of 261 mg/l, laboratory findings normalised within 4 days. Free gas within the peritoneal cavity can be detected on an abdominal radiograph. the signs created by the free intraperitoneal air can be further divided by anatomical compartments in relation to the pneumoperitoneum: bowel-related signs.
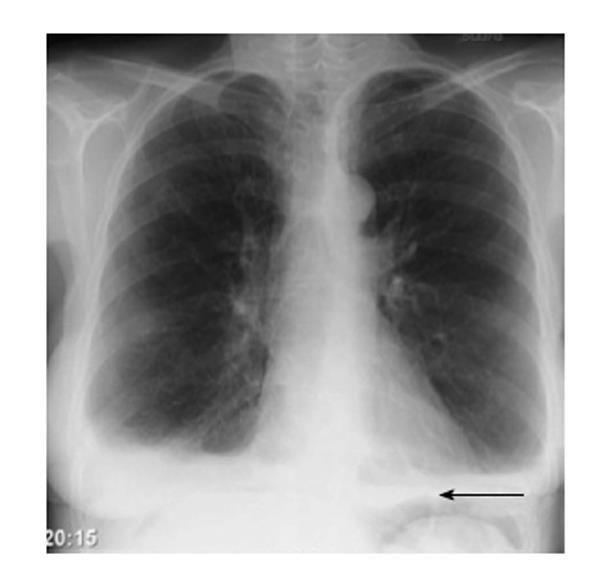
In suspected intussusception, an abdominal x-ray does not exclude intussusception but is useful in the differential diagnosis to exclude perforation or obstruction. [1] yet, ct scan is the best alternative for diagnosing intra-abdominal injury. Abdominal radiography will show many air-fluid levels, as well as widespread edema. acute ischemic abdomen is a surgical emergency. typically, treatment involves removal of the region of the bowel that has undergone infarction and subsequent anastomosis of the remaining healthy tissue. X with an incidence of 1 in 4000 births, esophageal atresia (ea) is a rare congenital anomaly in which the upper esophagus is not connected to the lower esophagus and the stomach. [1-3] it is prenatally diagnosed in 24% to 32% of the cases. [4-6] five types of ea are distinguished on the basis of the presence or absence of a tracheo-esophageal fistula (tef) and the length of the present. Free intraperitoneal air after surgery occurs in up to 60% of laparotomies and 25% of laparoscopic procedures 2. larger volumes of gas are associated with a smaller body mass index 3. clinical presentation. a tympanic percussion sound on percussion may be elicited on abdominal examination.
Acute perforation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Abdominal Xray Wikipedia

More intra abdominal free air x ray images. Pneumoperitoneum. frontal chest x-ray. the air bubble below the right hemidiaphragm (on the left of the image) is a pneumoperitoneum. pneumoperitoneum is pneumatosis (abnormal presence ray intra air abdominal free x of air or other gas) in the peritoneal cavity, a potential space within the abdominal cavity. the most common cause is a perforated abdominal organ, generally. This is a basic article for medical students and other non-radiologists. fat stranding is a sign that is seen on ct. it describes the change in attenuation of fat around an inflamed structure and is a very helpful signpost for intra-abdominal pathology.
Some studies have investigated an association between intra-abdominal free air and peritonitis in pd patients. however, most used chest x-rays, which are of limited sensitivity, and the association was not made clear. we conducted a retrospective study of the association between peritonitis and intra-abdominal free air using computed tomography. X-rays use beams of energy that pass through body tissues onto a special film and make a picture. they show pictures of your internal tissues, bones, and organs. bone and metal show up as white on x-rays. x-rays of the belly may be done to. Every time you check a chest x-ray you should make sure there is no free intra-abdominal air under the diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum). this is a sign of bowel perforation. pneumoperitoneum on an erect chest x-ray. Every time you check a chest x-ray you should make sure there is no free intra-abdominal air under the diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum). this is a sign of bowel perforation. pneumoperitoneum on an erect chest x-ray.
Abdominal and chest x-ray plain abdominal x-rays are often non-specific but may suggest the presence of an obstruction; faecal impaction and duodenal atresia can be detected on x-ray. in addition, if sufficiently radio-opaque, it may be possible to identify gallstones or urinary stones on a plain abdominal film. The free intra-abdominal air can outline the whole abdomen, i. e. football sign, or the falciform ligament of the liver, i. e. silver’s sign. the triangular collection of gas within the morison pouch is known as doge’s cap sign. A chest x-ray looks at the structures and organs in your chest. learn more about how and when chest x-rays are used, as well as risks of the procedure. due to interest in ray intra air abdominal free x the covid-19 vaccines, we are experiencing an extremely high call vol. Abdominal x-ray. although the erect chest x-ray is a much more sensitive investigation for pneumoperitoneum, there are several signs that may be useful in detecting free gas on an abdominal x-ray. rigler's/double wall sign. rigler's sign (also known as the double wall sign) is the appearance of lucency (gas) on both sides of the bowel wall.
How to treat free air in abdomen? when free air in abdominal x-ray is detected, it is generally an emergency. this is because it always indicates perforation somewhere in the hollow viscera of the abdomen. it can be in the stomach or in the intestine. on detection of air in abdominal cavity, patient is immediately rushed to hospital and in most cases exploratory laparotomy is performed to detect the site of perforation. Jun 17, 2021 · increasing intra-abdominal pressure elevates the diaphragm, which forcefully expels air from the lungs. contraction of the anterolateral abdominal wall also produces the force required for defecation micturition (urination), vomiting, and parturition (childbirth).
As you're sitting in the dentist's chair, you might be told you need a dental x-ray. here's what to expect with this painless procedure and why your dentist may recommend it. There is a large quantity of free air in this patient's abdomen. the image is obtained with the patient supine. free air has risen above the liver and bowel (red arrows). the air is not contained within any visible bowel wall.
